Search This Supplers Products:Plastic machinery, injection mouldInjection molding machineBlow molding machineHDPE extrusion machine
The Description of injection molding
time2018/10/11

- Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers.
Injection moulding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mould.
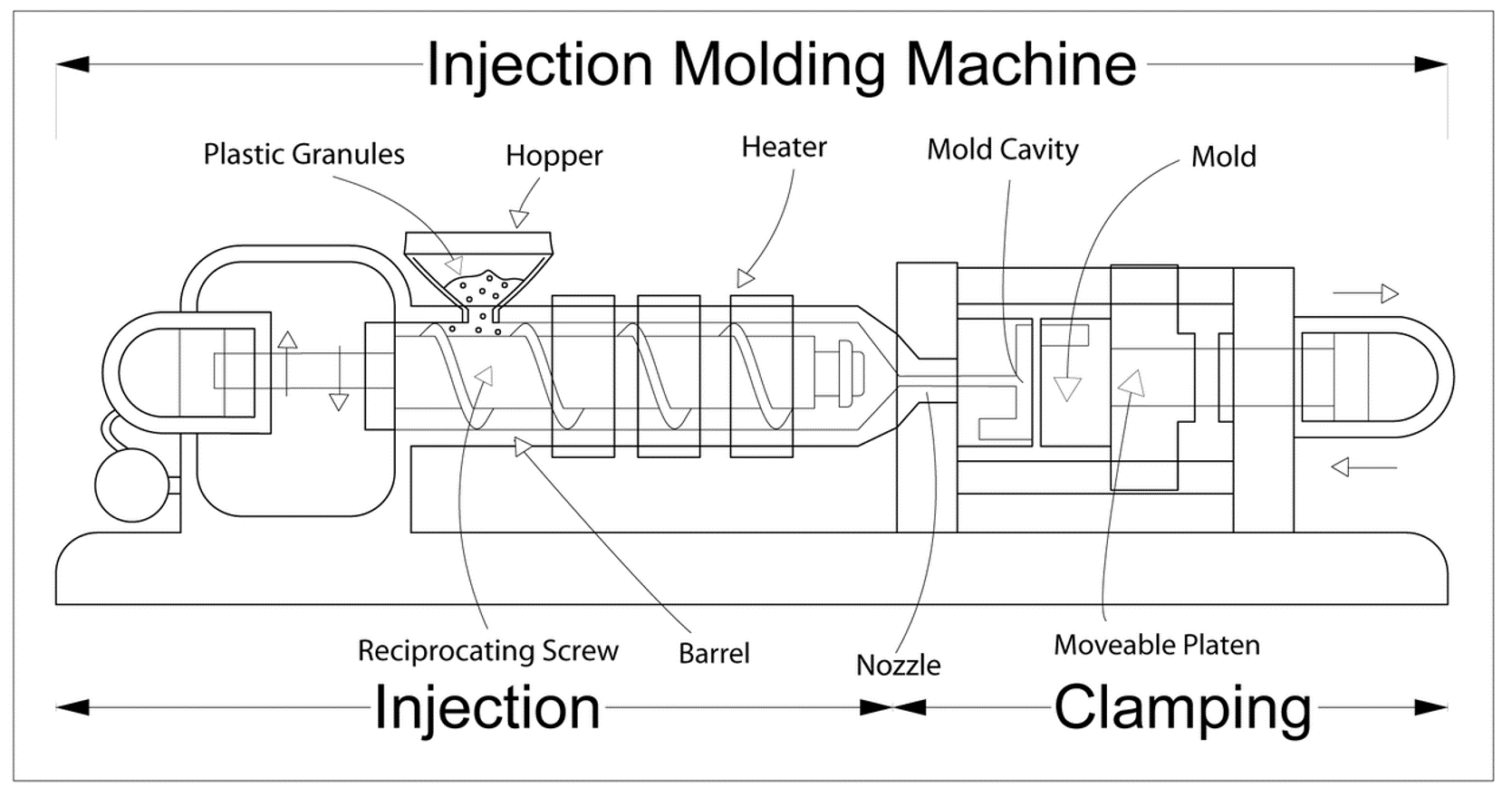
Injection moulding can be performed with a host of materials mainly including metals, (for which the process is called die-casting), glasses, elastomers, confections, and most commonly thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed (Using a helical shaped screw), and injected (Forced) into a mould cavity, where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity.[1]:240 After a product is designed, usually by an industrial designer or an engineer, moulds are made by a mould-maker (or toolmaker) from metal, usually either steel or aluminium, and precision-machined to form the features of the desired part. Injection moulding is widely used for manufacturing a variety of parts, from the smallest components to entire body panels of cars. Advances in 3D printing technology, using photopolymers which do not melt during the injection moulding of some lower temperature thermoplastics, can be used for some simple injection moulds.

Eight Steps to Perfect Parts
The plastic injection molding process can be summarized into eight steps:
Everything from colors and textures, to lettering, logos, and designs, to hinges and other functionality can be incorporated into the creation of a plastic part.
